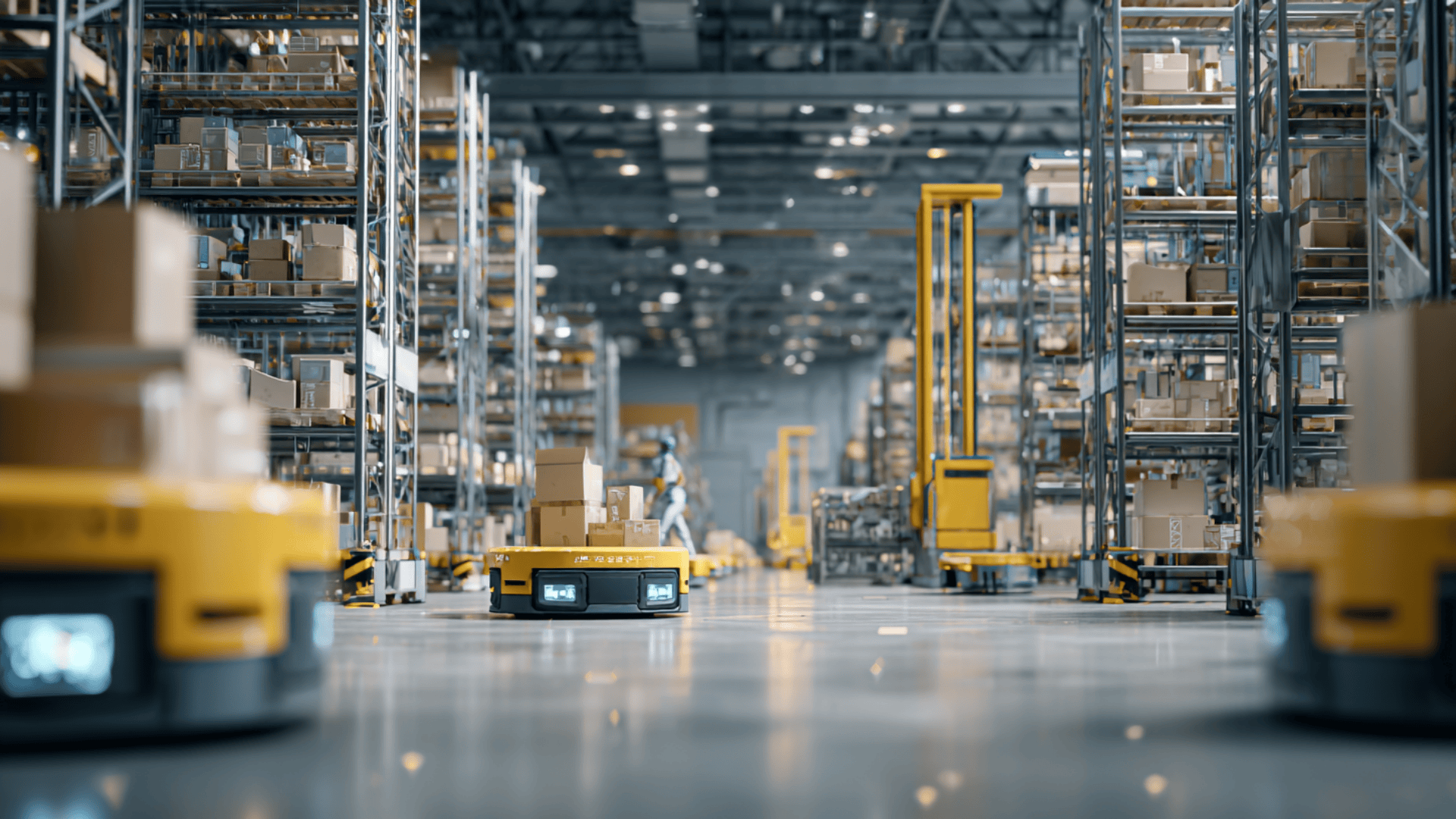
Logistics automation is quickly becoming the backbone of modern supply chains, helping companies run smarter and faster.
Instead of relying on slow, manual work, I’ve seen how businesses like yours can use connected tools to track inventory, move goods, and plan deliveries with a lot less stress.
The real value of automation shows up when all these tools work together, turning messy, manual processes into smooth and reliable systems.
For you, that could mean less time worrying about errors and more time focusing on growth. But before getting into the details, let’s start with the basics.
What is Logistics Automation?
Logistics automation is just a fancy way of saying you use technology to handle jobs that people used to do by hand.
Think about robots moving boxes in a warehouse, or software that keeps track of inventory so you don’t have to count every item yourself. I’ve seen how even small changes, like using scanners instead of clipboards, can save a ton of time.
This idea isn’t brand-new. Back in the day, businesses leaned on paper records and manual labor. Over time, barcodes, conveyor belts, and warehouse software started to take over. Now, we’ve moved into a world of AI, robotics, and smart systems that work almost nonstop.
You can see the difference when orders ship faster, errors drop, and workers focus on bigger tasks instead of repetitive ones.
Why Businesses are Turning to Logistics Automation Systems
I’ve noticed that most businesses turn to automation for the same reasons: they want to save time, cut costs, and get things right the first time.
When a system can handle repetitive work, you don’t have to worry as much about mistakes, delays, or wasted resources. You’ll see orders moving out faster, inventory updated in real time, and fewer headaches from lost or damaged shipments.
On the other hand, I know how tough manual logistics can be. Workers spend hours picking items, tracking stock, and filling out forms.
It’s easy to make errors when you’re tired or rushing, and even small slip-ups can snowball into big problems for customers. Automation helps smooth out those rough spots by keeping the process consistent and reliable.
Core Areas of Logistics Automation

When people talk about logistics automation, they usually break it down into a few main areas. I’ll walk you through the big ones so you can see where automation really makes a difference.
Warehouse Operations
Inventory Management
Keeping track of stock by hand is a nightmare. With automation, you’ll know exactly what’s on the shelf and when it needs to be restocked. Real-time tracking and analytics make it easier to avoid overstocking or running out. I’ve found that this alone can save businesses a lot of wasted money.
Transportation & Delivery
Getting products from point A to point B is often the hardest part. AI tools now plan routes, predict traffic delays, and keep deliveries on track. Last-mile solutions and even trucking automation are helping companies get goods to customers faster while cutting down on fuel and labor costs.
Fulfillment & Dock Management
Loading and unloading trucks by hand takes time and often causes delays. Automation steps in here with systems that organize dock schedules and equipment that handles heavy lifting. You’ll see faster turnarounds and fewer bottlenecks at busy facilities.
Top Logistics Automation Tools and Systems

There are a handful of tools that stand out in logistics automation right now. Each one focuses on solving a different part of the process, and together they cover almost everything a business needs to keep supply chains moving.
1. Data Capture Software
Data capture is the backbone of automation. Barcode scanners, RFID tags, and IoT sensors collect information about products in real time. This helps you know exactly where an item is, from warehouse shelf to delivery truck.
Some systems also track temperature and handling conditions, which are critical for food or medicine. Without this, you’d be relying on guesswork. With it, you have accurate records at every step.
2. Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics takes raw data and turns it into forecasts. Businesses use it to plan inventory, predict delivery delays, and even schedule maintenance before a truck or machine breaks down.
For example, if demand spikes during holidays, predictive tools help you stock up before shelves go empty. If you’ve ever had orders pile up because of poor planning, this kind of forecasting prevents it.
3. AI-Powered Robotics
Robotics is changing warehouses the most. Autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) move products across large facilities without needing a driver. Robotic arms can pick and pack faster than people, and they don’t get tired.
These tools reduce errors, speed up fulfillment, and free workers to handle more complex jobs. Some warehouses even use drones to scan inventory on high shelves, cutting down hours of manual work into minutes.
4. Cloud-Based Automation SaaS
Cloud platforms connect the dots between different systems. Instead of having separate software for inventory, transport, and fulfillment, SaaS solutions bring them all together.
5. Vendor Highlights
A few leading companies are pushing logistics automation forward with solutions tailored to different parts of the supply chain.
- KNAPP: Known for smart warehouse systems, including shuttles and automated picking solutions. Their tools improve accuracy in high-volume facilities.
- FarEye: Specializes in delivery management and real-time tracking. Companies use it to give customers live updates and optimize last-mile routes.
- Locus Robotics: Focuses on AMRs that work alongside humans. Their robots handle heavy transport inside warehouses, which cuts down walking time for staff and boosts productivity.
These vendors represent different strengths: KNAPP for storage and picking, FarEye for transport visibility, and Locus for robotics. Choosing the right one depends on where your biggest pain points are.
Industry Trends and Market Outlook
Logistics automation is growing fast, and the numbers show it’s not slowing down anytime soon.
Market Size and Growth Projections
The global market was valued at over $78 billion in 2024 and is expected to more than double in the next few years. Projections suggest it could pass $200 billion by 2030, driven by rising demand for faster deliveries and cost efficiency.
For businesses, that means more investment flowing into new tools and wider adoption across industries.
Innovations Shaping the Future
Several technologies are leading the way:
- AI and Machine Learning: Smarter forecasting, faster decision-making, and reduced errors.
- IoT Devices: Sensors that track goods in real time, from temperature to location.
- Robotics: Expanding beyond warehouses into transportation and last-mile delivery.
- Sustainability Solutions: Optimized routes, electric vehicles, and energy-efficient systems are helping reduce emissions.
These innovations aren’t just nice extras. They’re becoming standard in modern supply chains.
Insights from McKinsey, EY, and Fortune Business Insights
- McKinsey, in its analysis titled “Automation in logistics: Big opportunity, bigger uncertainty“, highlights both the high automation potential in logistics and the uncertainties, such as workforce impacts and investment risks.
- EY’s report “Automation in the logistics sector” explains how automation and AI are reshaping trucking and transport operations in response to rising costs and supply challenges.
- Fortune Business Insights, in its report “Logistics Automation Market Size, Share & Growth Report,” notes that the global logistics automation market was valued at USD 78.20 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 212.81 billion by 2032, with a CAGR of 13.4%.
The bottom line: automation is moving from optional to essential, and businesses that adapt early will likely stay ahead.
Automation Implementation Roadmap
If you’re thinking about adopting logistics automation, it helps to follow a clear path. I’ve broken it down into simple steps so you can see what matters most.
Step-by-Step Guide for Adopting Automation
- Assess your needs: Start by identifying where you struggle most, whether it’s inventory errors, slow picking, or delivery delays.
- Set goals: Decide what you want automation to achieve. Faster shipping? Lower labor costs? Better accuracy?
- Choose the right tools: Match solutions to your goals. For example, if accuracy is the issue, you may need RFID and data capture tools.
- Start small: Pilot automation in one area, like a warehouse zone, before rolling it out everywhere.
- Train your team: I’ve found that workers adjust better when they know how the system helps them, not just replaces tasks.
- Track results: Measure speed, accuracy, and savings to see if you’re hitting your goals.
Cost Considerations and ROI
Automation often means a big upfront investment. Robots, software, and sensors aren’t cheap, but they usually pay off over time. You’ll see savings in labor, fewer errors, and lower shipping costs.
ROI depends on how well the system is used; some companies see returns within a year, while others may take longer. Think of it as spending more now to spend less later.
Integration with Existing Systems (ERP, WMS, TMS)
The biggest challenge I’ve noticed is making new automation work with the systems you already use, like ERP, WMS, or TMS platforms.
Look for solutions that connect easily to your setup so data flows across every stage: orders, inventory, and transport. When everything talks to each other, you avoid silos and get a single, accurate view of your supply chain.
Case Studies and Real-World Examples
Sometimes the best way to see the value of logistics automation is through real stories. I’ve noticed that the results can look very different depending on the size of the business.
Small Business Use Cases
For smaller companies, automation often starts with simpler tools like barcode scanners, RFID tags, or cloud-based inventory software.
I’ve seen small retailers use these to keep tighter control of stock and avoid costly errors. Even a modest system can cut down on lost sales from stockouts and save hours of manual counting each week.
Large Business Use Cases
Larger companies usually go further with robotics, AS/RS systems, and AI-driven route optimization.
One global distributor I read about cut their warehouse labor costs by nearly 30% after rolling out robotic picking systems. Big players often see the fastest improvements because their scale makes every small efficiency add up.
ROI and Performance Outcomes
Returns vary, but automation almost always pays off. Small businesses might see a quick ROI in less than a year just by reducing errors and speeding up stock counts. Larger firms often see savings in labor and transport costs that add up to millions over time.
The common theme is that once automation is in place, both accuracy and speed go up, while costs go down.
Challenges and Risks of Automation
While automation brings a lot of benefits, it’s not without hurdles. I know of businesses that ran into a few common issues when making the switch.
- Job shifts and reskilling: Manual roles shrink, but new tech roles grow. Training helps workers adapt instead of falling behind.
- Cybersecurity risks: More data flow means higher attack risk. Firewalls, encryption, and updates are a must.
- High upfront costs: Robots and software need big investment. Smaller firms feel this the most.
- System downtime: Breakdowns can stop operations. Maintenance plans reduce costly delays.
- Integration hurdles: New tools may not fit old systems. Careful planning avoids workflow issues.
- Change resistance: Teams may resist automation. Clear communication builds trust and support
Sustainability and the Future of Logistics Automation
When I think about logistics automation, I don’t just see faster shipments or fewer mistakes. I also see a real chance to make supply chains greener. And honestly, that’s something more businesses (and customers) are paying attention to.
Automation isn’t just about speed. Smarter systems cut fuel use by planning routes that avoid wasted miles.
Warehouses using automated storage often use less energy because space is tighter and climate control is more efficient. Even little things, like switching from paper logs to digital tracking, chip away at unnecessary waste.
But the bigger story is how automation fits into green supply chains. Electric trucks are starting to replace diesel fleets. IoT sensors monitor carbon output so businesses can track their footprint in real time.
Some companies are even using robotics designed to run on less energy. The result is supply chains that aren’t just efficient; they’re cleaner.
If you’re weighing automation for your business, think about both the financial payoff and the environmental one. Cutting costs feels good, but showing customers that you’re serious about sustainability can set you apart in ways money alone can’t.
Conclusion
Logistics automation is moving fast, and the businesses adopting it now are the ones staying ahead.
I’ve seen how even small changes, like automating stock checks or streamlining routes, can save time and money while cutting down on errors. For you, that could mean smoother operations and happier customers.
If you’re curious about what’s next, don’t stop here. Take a look at my other blogs where I share practical tips on supply chain trends, transport solutions, and smart tools you can use.
The more you learn, the easier it gets to spot opportunities for your own business. Start small, keep building, and let automation work for you instead of against you.















