In today’s digital world, having a reliable home network is more important than ever. Whether you’re working from home or controlling your devices, a well-configured network keeps everything running smoothly.
But setting up a home network can be tricky, especially with so many devices and connection options available.
In this blog, I’ll break down the essentials of building a home network, from understanding the core components like modems and routers to expanding your coverage and ensuring security.
I’ll also tell you how to optimize your network for the best performance. Let’s make your home network both powerful and secure.
What is a Home Network and Why It Matters
A home network is a system that connects all your digital devices, such as computers, smartphones, smart TVs, gaming consoles, and IoT gadgets, to each other and to the internet.
It can be wired, using Ethernet cables, or wireless, through Wi-Fi. Think of it as the digital backbone of your household: it allows every device to communicate, share resources, and access the web simultaneously.
How the Setup Enables Sharing and Connectivity
- Shares Internet Access: Multiple devices can go online at once using the same internet connection.
- Allows Device-to-Device Communication: Send a file from your laptop to your desktop, stream a movie from your media server to your TV, or print from any device connected to the network.
- Integrates Smart Devices: Connects smart bulbs, thermostats, and security cameras so they work together.
- Simplifies Convenience and Control: Centralized management through your router or mobile app lets you monitor connections, control bandwidth, and secure your network.
You can visualize the setup like this:
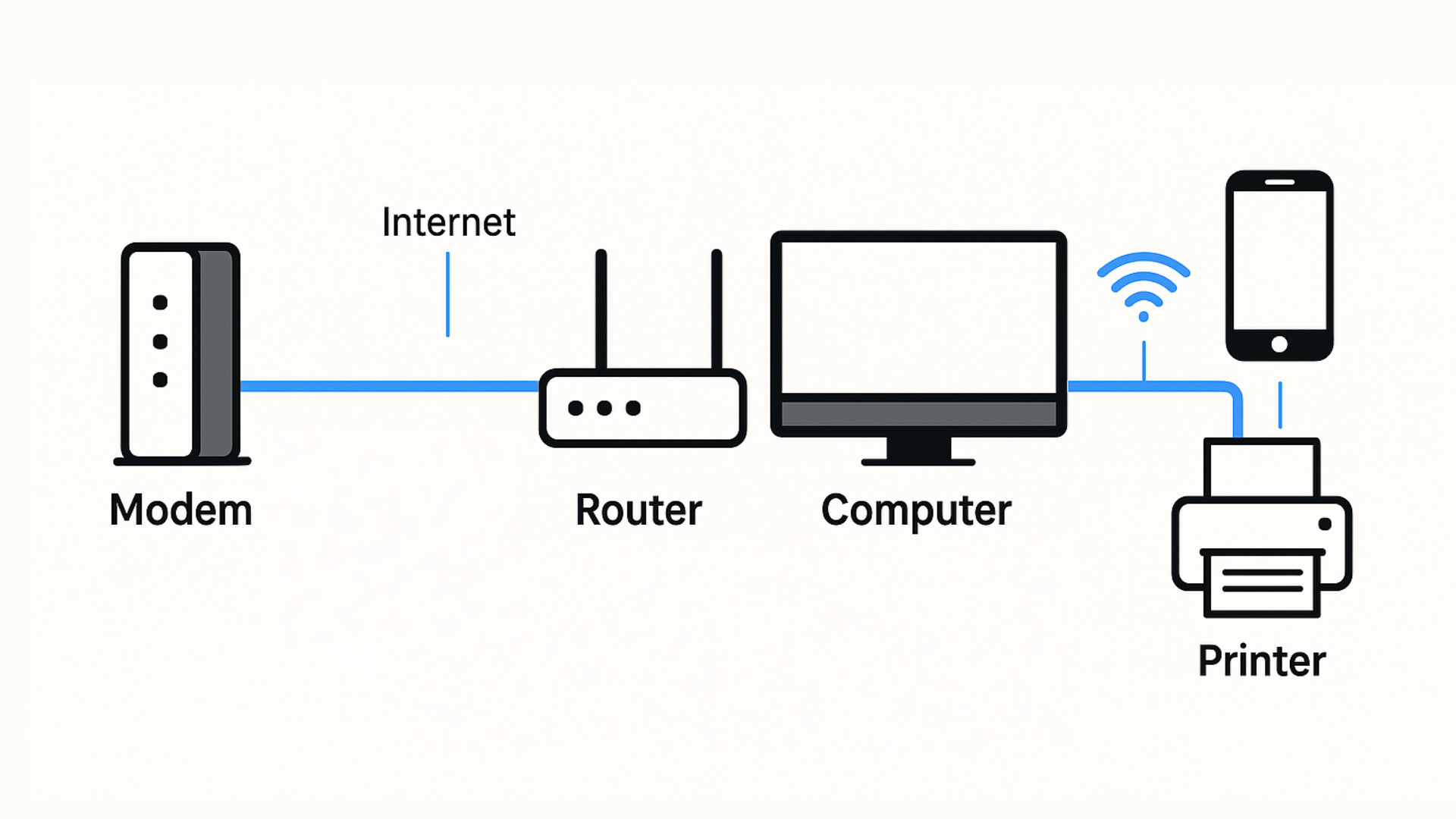
Explanation:
- The modem connects your home to your internet service provider (ISP).
- The router distributes the internet connection to devices either wirelessly (Wi-Fi) or via Ethernet cables.
- A switch can expand wired connections for more devices.
- Every device, whether wired or wireless, communicates within this network to share files, media, and internet access.
Core Components of a Typical Home Network
Your home network relies on several key components that work together to connect your devices to the internet and to each other.
1. Modem – The Internet Gateway
The modem is your home’s bridge to the internet.
- It connects directly to your Internet Service Provider (ISP) through a cable or fiber line.
- Its job is to translate signals from your ISP into data that your home devices can understand.
- You typically receive the modem from your ISP, though you can also buy your own for better performance or to avoid rental fees.
Tip: If your modem has built-in Wi-Fi, it’s a modem-router combo, but for greater control and performance, most users prefer separate devices.
2. Router – The Network Creator
The router takes the internet signal from your modem and creates your local network (LAN).
- It allows multiple devices like laptops, smartphones, smart TVs, and more to connect simultaneously.
- Modern routers broadcast Wi-Fi signals while also offering Ethernet ports for wired connections.
- It also handles traffic management, security settings, and firewall protection.
Think of it as the control center of your home network, managing who gets access and how data flows.
3. Switches, Access Points, and Mesh Nodes – Network Expanders
These devices help extend and strengthen your network beyond the main router.
- Switches: Used to expand wired connections. Ideal for connecting multiple desktop PCs, gaming consoles, or NAS drives in one area.
- Access Points (APs): Extend Wi-Fi coverage to additional areas; perfect for large homes or multi-story buildings. They connect to the main router via Ethernet.
- Mesh Nodes: Work together as a team of routers, creating a single, seamless Wi-Fi network across your entire home. They automatically direct your devices to the strongest signal as you move around.
In short, Switches expand your wired network, access points boost wireless coverage, and mesh nodes ensure consistent connectivity everywhere.
4. Devices – The Endpoints That Matter
Every connected device in your home relies on the network to function efficiently. Examples include:
- Computers & Laptops – for browsing, streaming, work, and gaming.
- Smart TVs – for streaming services and media sharing.
- IoT & Smart Home Devices – thermostats, lights, cameras, speakers.
- Printers & NAS Drives – for file sharing and storage across the network.
Pro Tip: Group devices by function; entertainment, work, smart home, and assign them to different Wi-Fi bands or VLANs for smoother performance and security.
Types of Home Networks
Home networks come in three main types: wired, wireless, and hybrid. Each has its own advantages and ideal use cases, and most modern homes benefit from a mix of both Ethernet and Wi-Fi connections.
1. Wired Networks
A wired home network uses physical Ethernet cables to connect devices directly to your router or switch. It provides stable, high-speed connections that are ideal for demanding tasks and fixed devices.
Setup Guide:
- Run Ethernet cables (Cat6 or Cat7) from your router to each device or to a network switch.
- Plug each cable securely into your devices’ Ethernet ports.
- Confirm connectivity through your device’s network settings or router dashboard.
- Optionally, use wall outlets or in-wall wiring for a cleaner installation.
Pro Tip: For a neat setup, use wall-mounted Ethernet jacks or in-wall cabling for permanent installations.
2. Wireless Networks
A wireless network (Wi-Fi) connects devices through radio signals rather than cables, offering mobility and convenience throughout the home.
Setup Guide:
- Place your router in a central, elevated position to maximize signal range.
- Log in to the router’s admin panel and set your SSID (Wi-Fi name) and secure password.
- Connect your devices to the Wi-Fi network using those credentials.
- If coverage is weak, add mesh nodes or wireless access points in low-signal areas.
Avoid Common Issues:
- Interference: Keep the router away from microwaves, cordless phones, or thick walls.
- Signal drops: Use mesh Wi-Fi systems or access points to strengthen coverage.
- Congestion: Use dual-band or tri-band routers to balance traffic across 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, and Wi-Fi 6/7 bands.
3. Hybrid Networks
A hybrid home network blends both wired and wireless connections for optimal flexibility, using Ethernet for high-performance devices and Wi-Fi for mobile or smart devices.
Setup Guide:
- Connect your router to key devices (like PCs or TVs) using Ethernet cables.
- Enable Wi-Fi for portable devices like phones, tablets, and IoT gadgets.
- Expand the network with switches for more wired ports or mesh nodes for broader wireless coverage.
- Manage all devices through your router’s dashboard or a dedicated app.
Pro Tip: Many smart homes today use hybrid networks to ensure seamless connectivity for everything from workstations to smart thermostats and voice assistants.
Comparing Benefits and Ideal Use Cases
| Network Type | Key Benefits | Ideal Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Wired | Fastest speed, minimal lag, highly secure, no interference | Gaming setups, home offices, streaming devices, NAS servers |
| Wireless | Easy setup, flexible device movement, no cabling required | Smartphones, tablets, laptops, smart home devices |
| Hybrid | Balanced performance and flexibility, scalable coverage | Mixed households, smart homes, multi-story homes, small offices |
Step-by-Step Home Network Setup Guide
Setting up your home network involves just a few key steps. Follow this simple process to get your devices online quickly and reliably:
1. Choose an Internet Service Provider (ISP) and Connect the Modem
- Select a reliable ISP that meets your speed and data needs.
- Once installed, connect the modem to your wall outlet or fiber/cable line, plug in the power, and wait for the signal lights to stabilize.
- Then, use an Ethernet cable to connect the modem to your router’s WAN (Internet) port.
2. Configure Your Router
- Turn on the router and connect to it using your computer or phone.
- Open the setup page in your browser (the IP address is usually printed on the device).
- Choose a network name (SSID), create a strong password, and select your Wi-Fi bands: 2.4 GHz for range and 5 GHz or Wi-Fi 6/7 for faster speeds.
- Save your settings and restart the router.
3. Connect Your Devices
Use Ethernet cables for stationary devices like desktop computers, smart TVs, and gaming consoles.
For wireless devices such as laptops, smartphones, and smart home gadgets, open Wi-Fi settings, select your network, and enter the password.
4. Test and Optimize Your Connection
Run an online speed test to check performance against your plan. If speeds are low, try repositioning your router, adding mesh nodes, or updating the firmware.
Regularly restarting your modem and router also helps maintain stability and performance.
Improving and Expanding Network Coverage
Once your home network is set up, you may find some rooms or floors with weaker signals or slower speeds. Expanding your coverage ensures every corner of your home stays connected.
Use a Mesh Wi-Fi System
Mesh Wi-Fi systems use multiple connected devices (called nodes) to create one continuous network. They eliminate dead zones and automatically direct your devices to the strongest signal.
Setup Tips:
- Place the main node near your router and others midway toward low-signal areas.
- Keep nodes in open, elevated spots away from thick walls or large appliances.
- Use a single network name (SSID) for seamless roaming.
Extend with Ethernet and Switches
For high-speed and stable connections, add Ethernet cables to connect stationary devices or access points.
If you need more wired ports, use a network switch to expand connectivity. This approach works best for home offices, gaming systems, and smart TVs.
Optimize Router Placement
Router location has a major impact on coverage. Keep it in a central, open area, ideally raised off the floor and away from obstructions. Avoid placing it near microwaves, cordless phones, or thick walls that block signals.
Tip: Use your router’s mobile app or built-in signal map to check weak zones and reposition devices for better performance.
Securing Your Network

Here are key steps to keep your home network secure from unauthorized access and online threats:
1. Change Default Credentials:
The default username and password for your router are often easy to guess. Change these to a strong, unique combination to protect your network from unauthorized access.
2. Enable WPA3 Encryption:
WPA3 is the latest Wi-Fi security protocol. It provides stronger encryption than WPA2, making it harder for attackers to intercept data or gain access to your network. Always enable WPA3 if supported by your router.
3. Update Firmware:
Router manufacturers regularly release firmware updates to patch security vulnerabilities and improve performance. Check for updates in your router’s admin settings and apply them regularly.
4. Use Firewalls:
Enable the firewall feature on your router. This acts as a barrier to block unwanted external traffic and prevent potential hackers from gaining access to your network.
5. Bonus: Zero Trust Access (Advanced Users):
Zero Trust is a security model where you never trust any device, even within your network. You verify everything before granting access, adding an extra layer of protection for sensitive data and devices.
This is especially useful for advanced users who need to secure multiple smart devices or home servers.
Integrating Smart Devices and Managing Network Traffic
Integrating smart home devices (IoT) into your network adds convenience but requires careful management to avoid security risks and congestion.
1. Connecting IoT Devices Securely
Use strong, unique passwords for each device and ensure their firmware is updated regularly. To improve security, segregate IoT devices on a separate network to minimize risks.
2. Setting Up Separate Guest Networks
Set up a guest network to provide internet access to visitors while keeping them away from your main devices. Limit access so guest devices can’t communicate with your primary network.
3. Managing Device Priority (Quality of Service Settings)
Use Quality of Service (QoS) to prioritize bandwidth for important devices like gaming consoles or work devices. Adjust these settings in your router’s admin panel to optimize performance during peak usage.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Here are common home network issues and quick solutions to resolve them:
Wi-Fi Drops
If your Wi-Fi keeps disconnecting, it may be due to interference, poor signal range, or router overload.
Solution:
- Reposition your router to a more central location and higher elevation.
- Change the Wi-Fi channel in your router’s settings to avoid interference.
- Restart the router to reset connections.
Slow Speeds
Slow internet speeds can be caused by overloaded networks or poor connection quality.
Solution:
- Test your speed using a tool like Speedtest.net to check against your plan’s speed.
- Limit the number of active devices during heavy usage.
- Switch to a wired connection for stationary devices like PCs or TVs for more stability.
- Upgrade your router to a newer model that supports higher speeds.
Device Conflicts
Device conflicts can cause network issues when devices fight for the same resources or IP address.
Solution:
- Reboot the device to refresh its connection.
- Set static IP addresses for critical devices like gaming consoles or printers.
- Check for firmware updates on your router to ensure it’s handling devices correctly.
Future-Proofing Your Network
Future-proofing your network means upgrading to equipment and solutions that will support new devices, faster speeds, and growing demands. Here’s how to make sure your network is ready for the future:
| Future-Proofing Strategy | Benefits | Tips |
|---|---|---|
| Upgrading to Wi-Fi 7 Routers | Faster speeds, lower latency, better bandwidth management for multiple devices | Look for tri-band support (2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, and 6 GHz) for optimal performance |
| Using Multi-Gig Ethernet | Faster wired connections, better for high-bandwidth tasks like gaming and streaming | Ensure multi-gig ports on routers, switches, and devices to fully benefit |
| Backups with NAS or Cloud Syncing | Secure data storage, easy access, protection against data loss | Use a hybrid approach: NAS for local backups and cloud for off-site protection |
Recommended Tools & Equipment
Here’s a selection of the best networking equipment available in the U.S., with tiered options for different budgets, from high-end routers and mesh systems to essential cables:
| Product | Description | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| ASUS RT‑BE96U Wi-Fi 7 Router | Premium Wi-Fi 7 router, future-proofing for large homes. | Power users, large homes, high-demand environments |
| Netgear Orbi 370 Mesh Wi-Fi System | Mesh Wi-Fi system with Wi-Fi 7 for seamless, whole-home coverage. | Large homes, multi-floor setups |
| TP-Link Archer BE9700 Wi-Fi 7 Router | Value Wi-Fi 7 router for fast speeds and high performance. | Mid-range homes, users needing a good value router |
| Google Nest WiFi Pro Mesh System | Easy-to-use mesh Wi-Fi system with smart home integration. | Smart homes, user-friendly setups |
| ASUS RT‑AX55 Wi-Fi 6 Router | Budget-friendly Wi-Fi 6 router, ideal for smaller homes. | Budget-conscious users, small homes |
| TP-Link TL‑SG108 8-Port Gigabit Switch | 8-port gigabit switch for wired connections. | Expanding wired network for multiple devices |
| Cat6a Ethernet Cable 5-m Pack | High-quality Ethernet cables for stable wired connections. | All devices requiring wired connectivity |
Wrapping Up
A well-set-up home network is essential for seamless connectivity, whether you’re working, gaming, or managing smart devices.
By understanding the core components like your modem, router, and switches, you can optimize your network for speed, security, and convenience.
With the right tools, you’ll enjoy reliable internet access and easy device communication throughout your home. Don’t forget to secure your network and manage your devices for the best experience.
Start upgrading your network today and enjoy smoother, faster connections for all your devices.